Overview
Content is key.
Common Errors
Common Faults
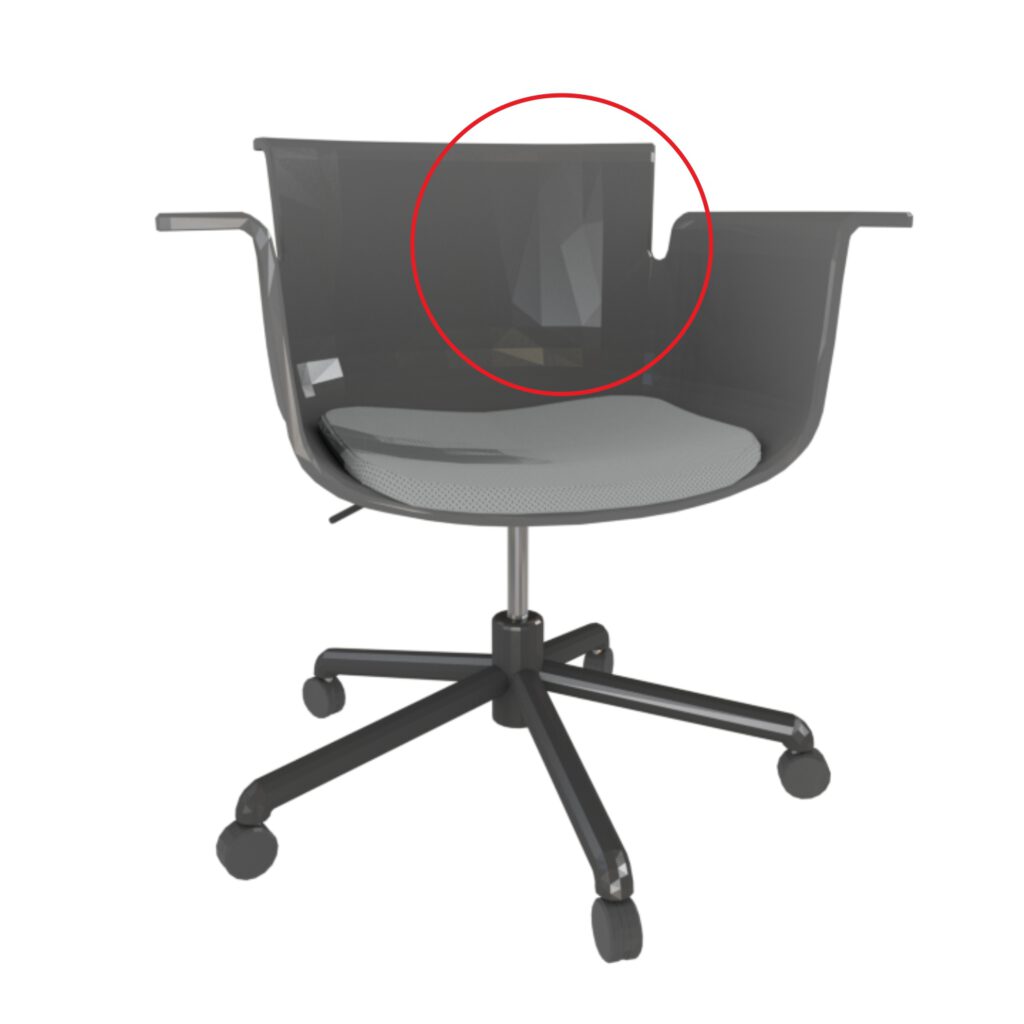

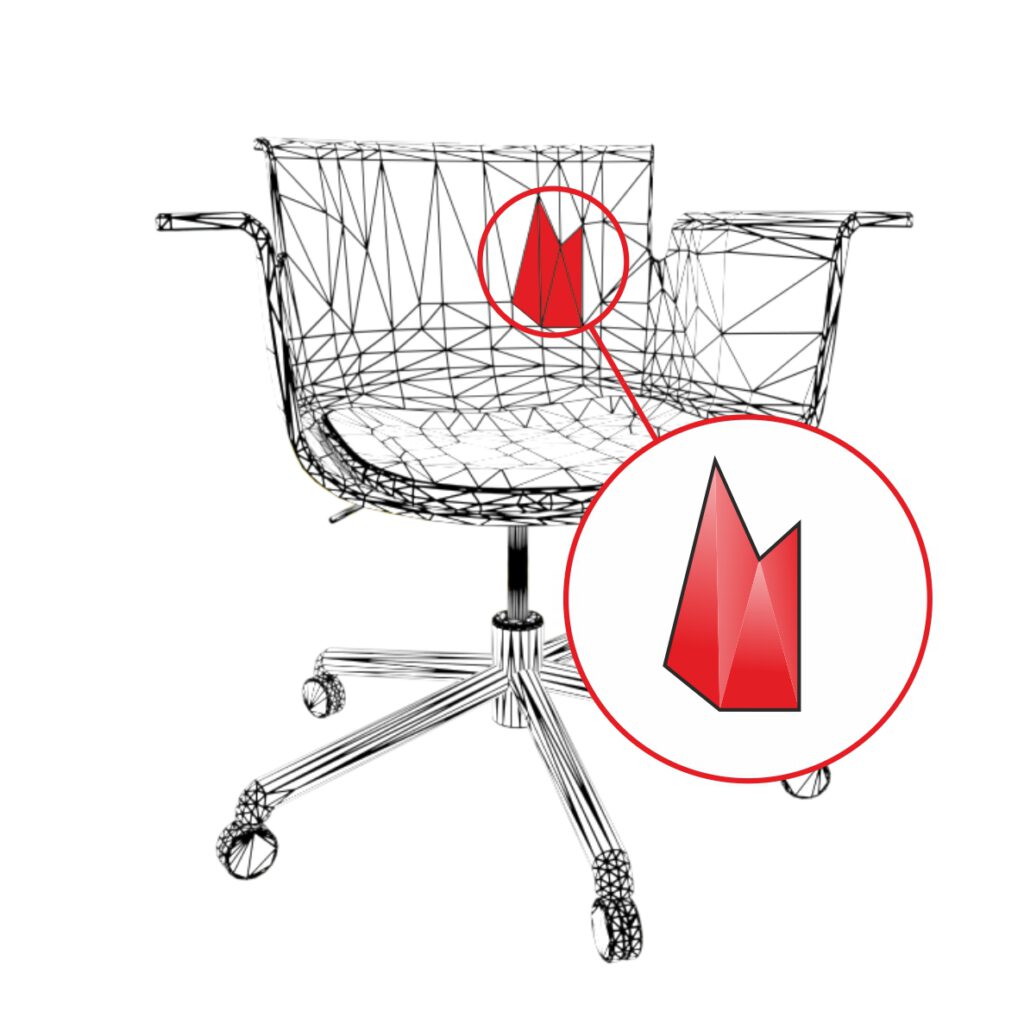
Faceted Surfaces
Vertex normals of faces are not blending into the direction of the adjacent face‘s normals. Shading of faces is calculated individually which results in visible facets.

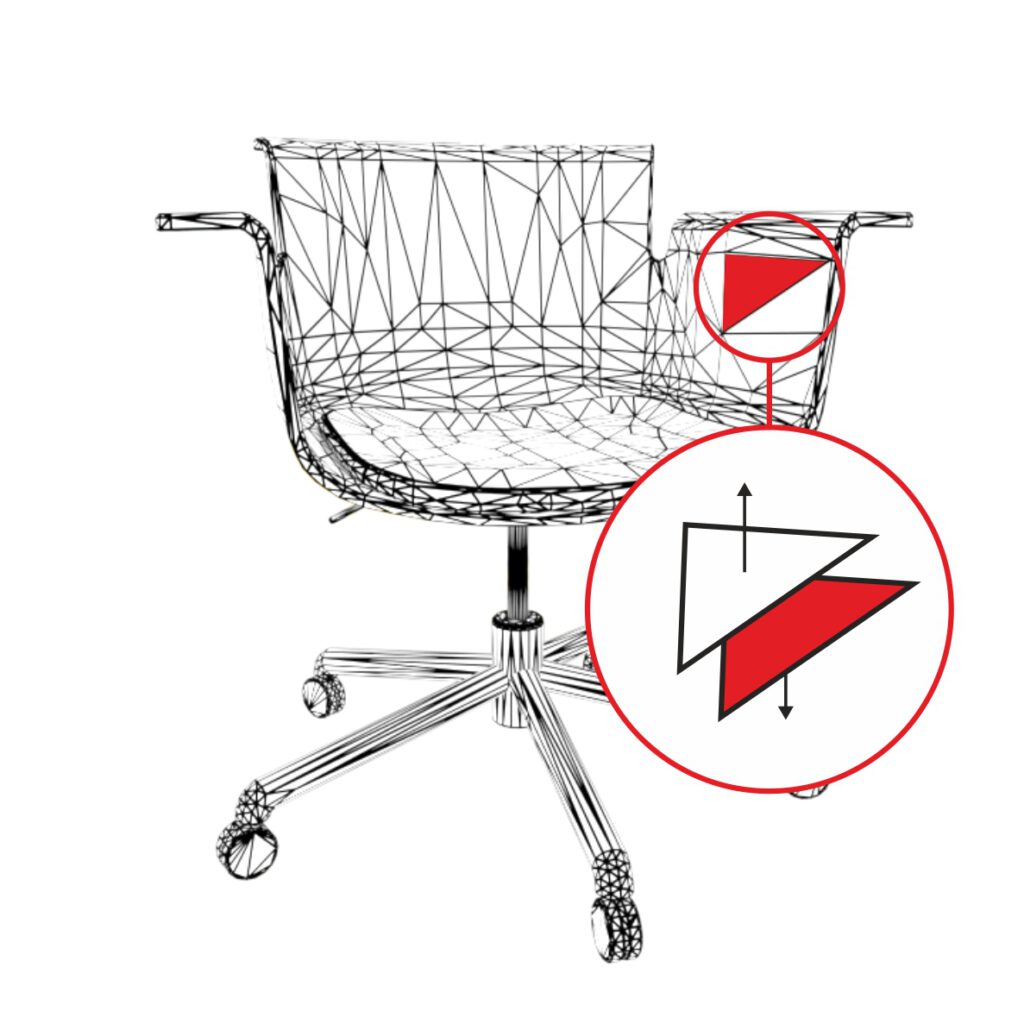
Flipped Faces

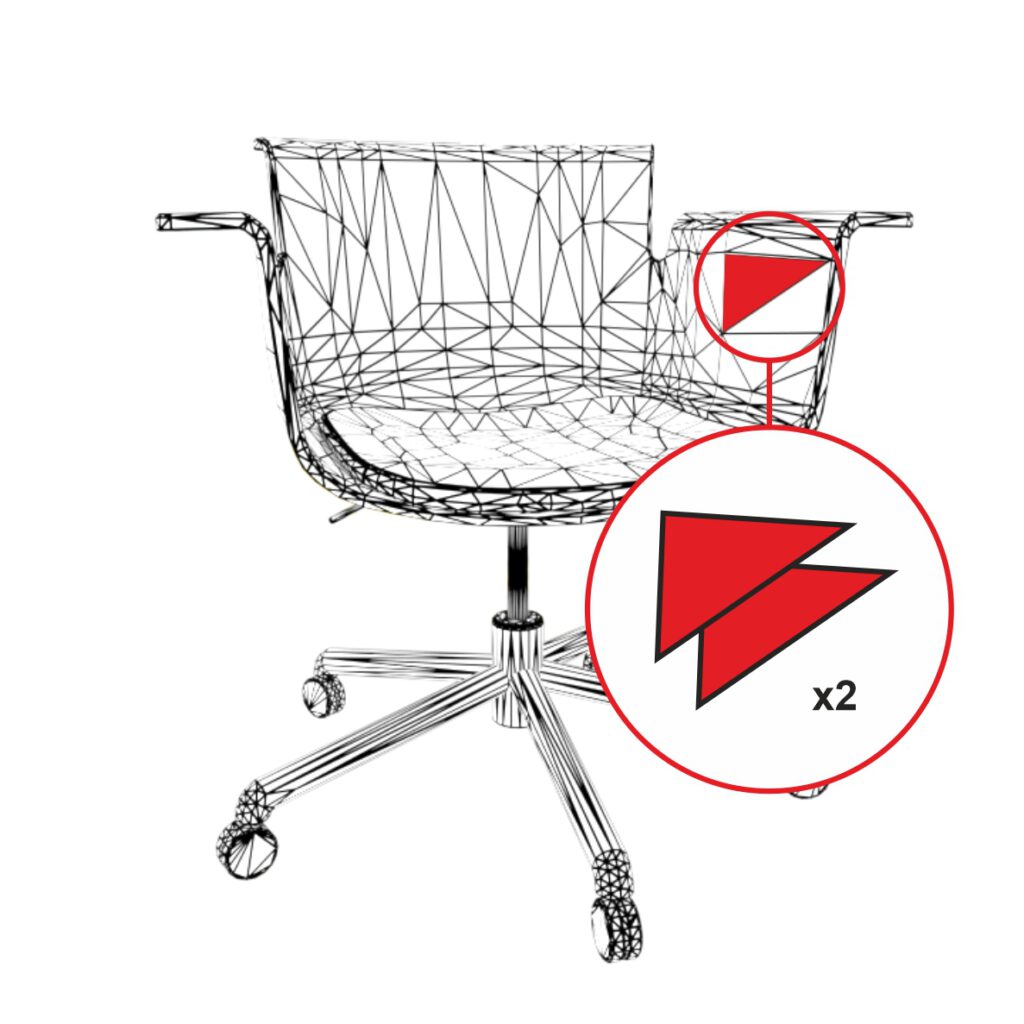
Duplicate Faces
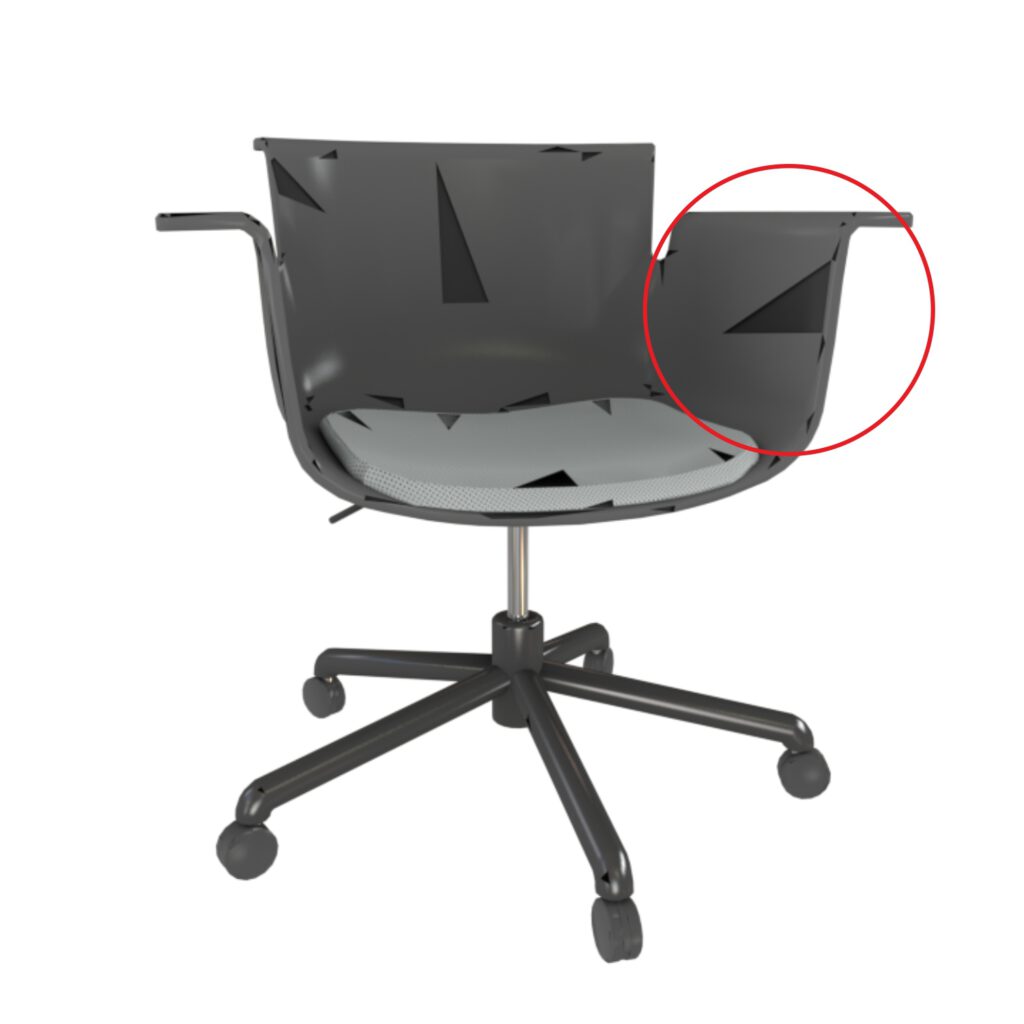

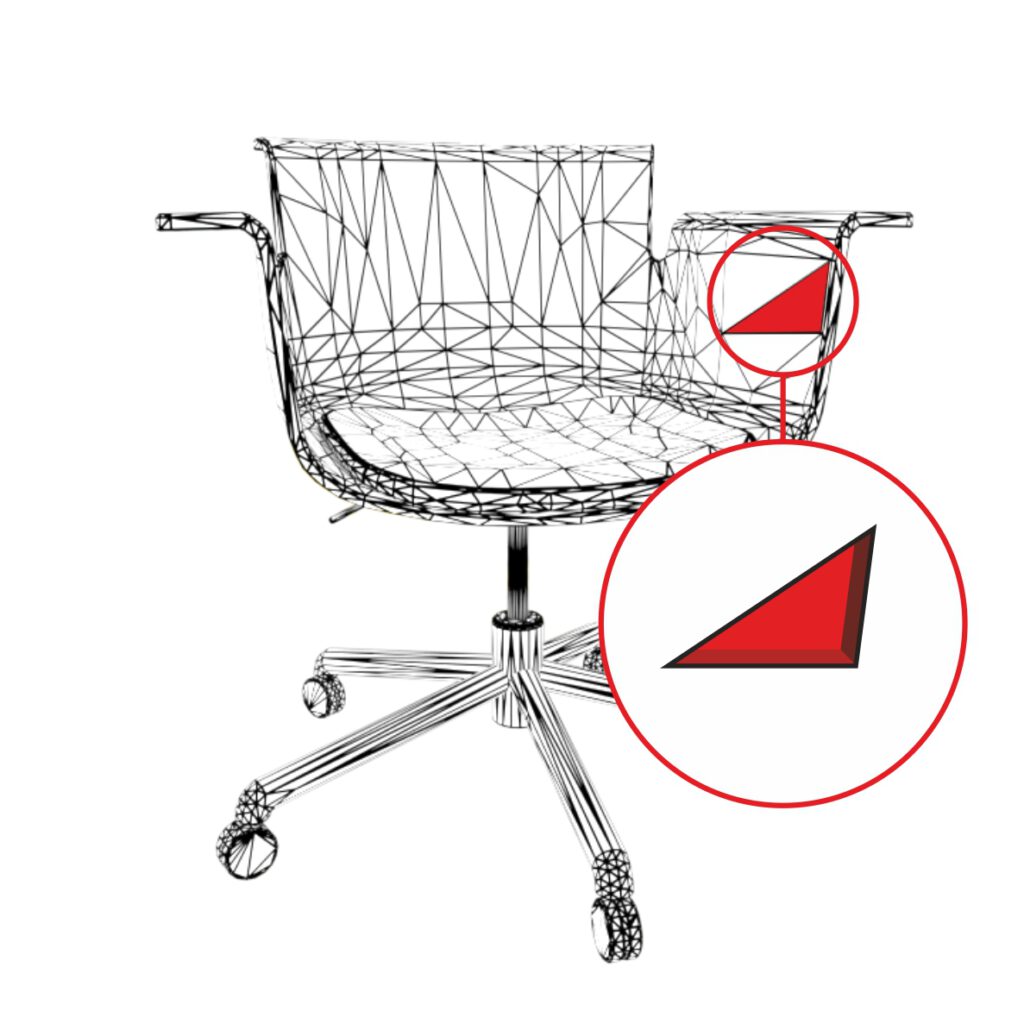
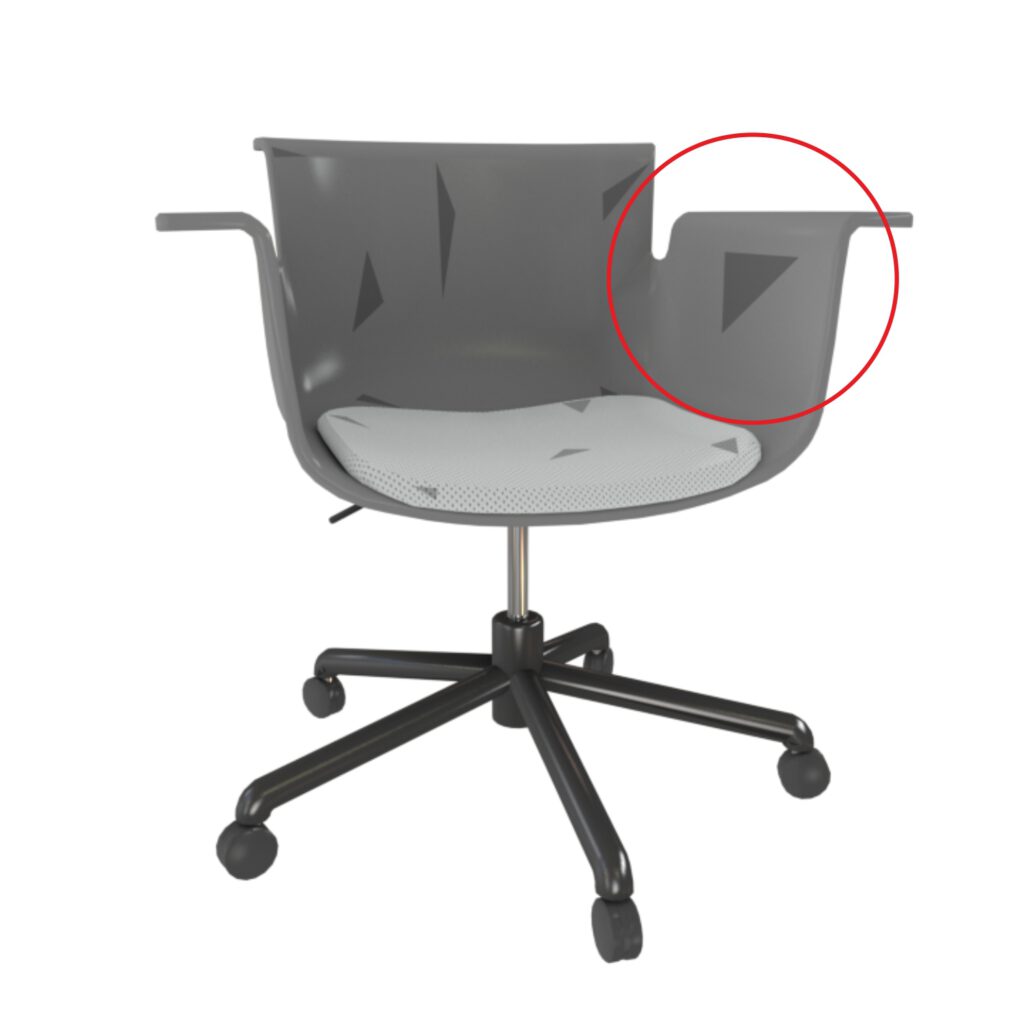
Missing geometry
Missing geometry is often due to creation software export settings or triangulation / polycount ratio. Faces seen through the hole might not show as they are facing outwards (backface culling).

Incorrect Mapping
Projected and stretched UV mapping causes distorted placement of textures on the object.


UV Orientation

Visible Tiling
Unevenly lit textures or untileable images show repeating visible patterns.
Best Practice
Best Practice

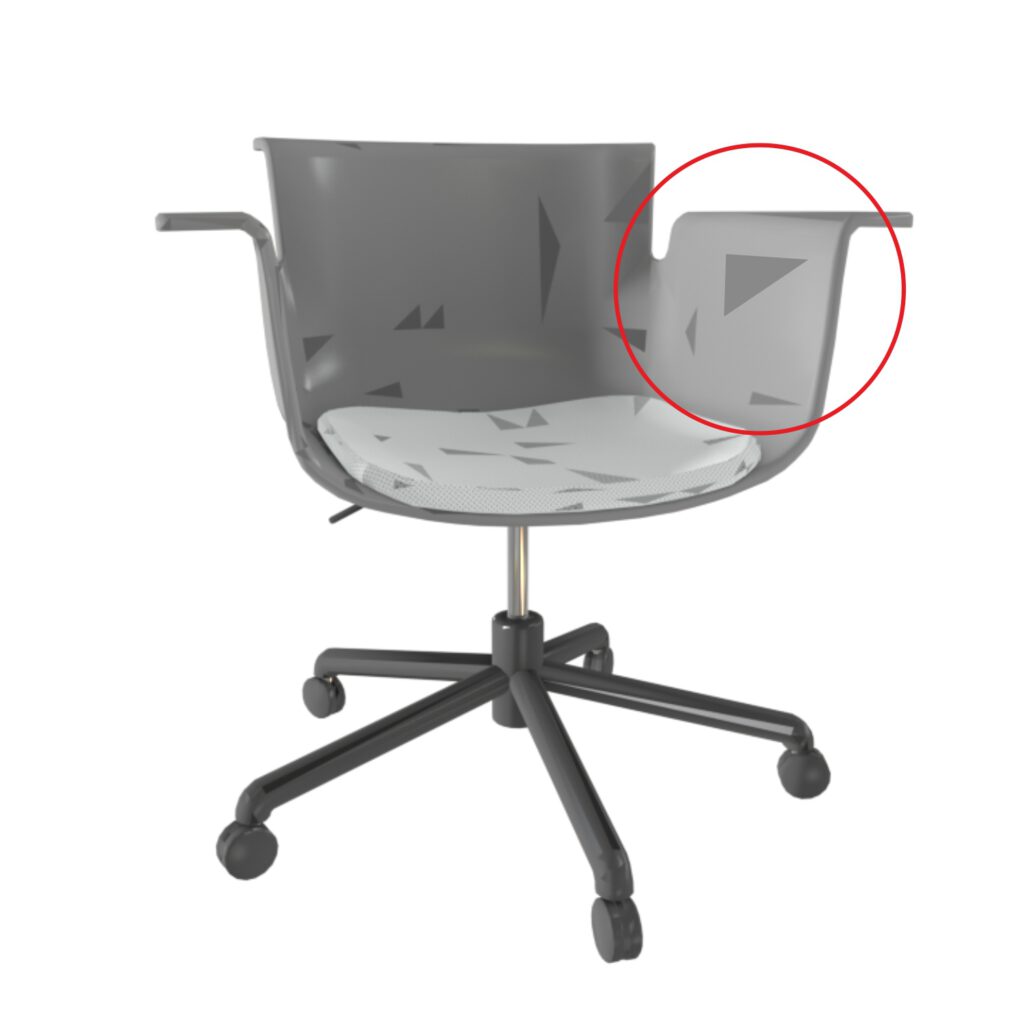
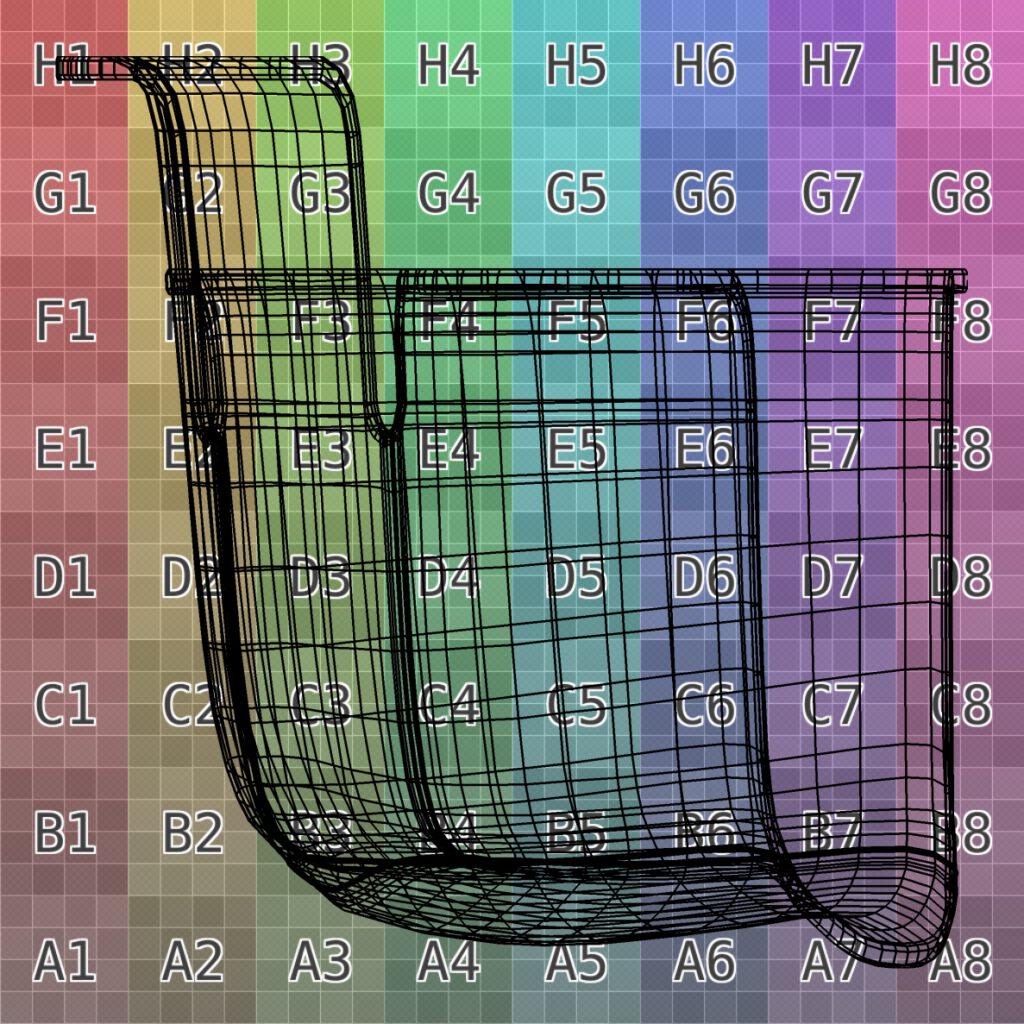
Smooth Surfaces
Unified vertex normals share the same direction between adjacent faces. A surface appears smooth, even with low geometry resolution.
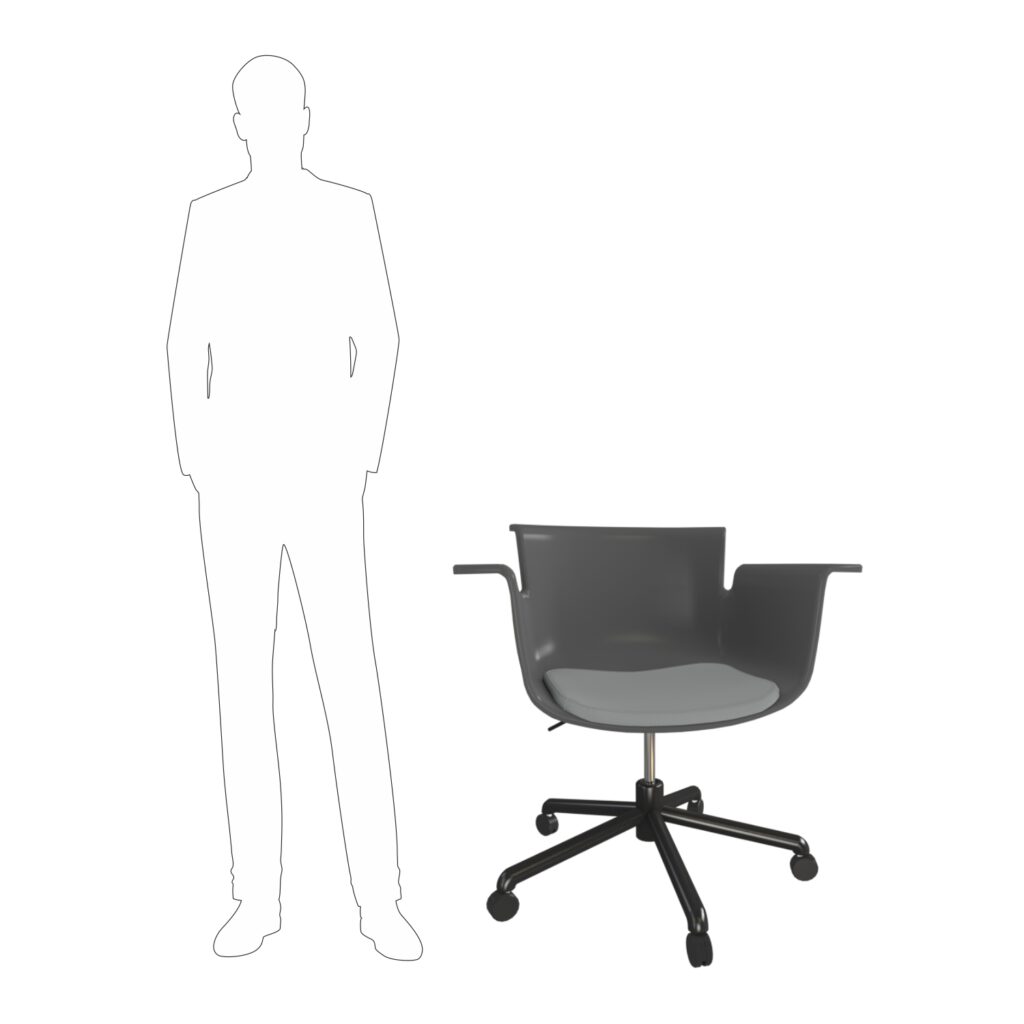


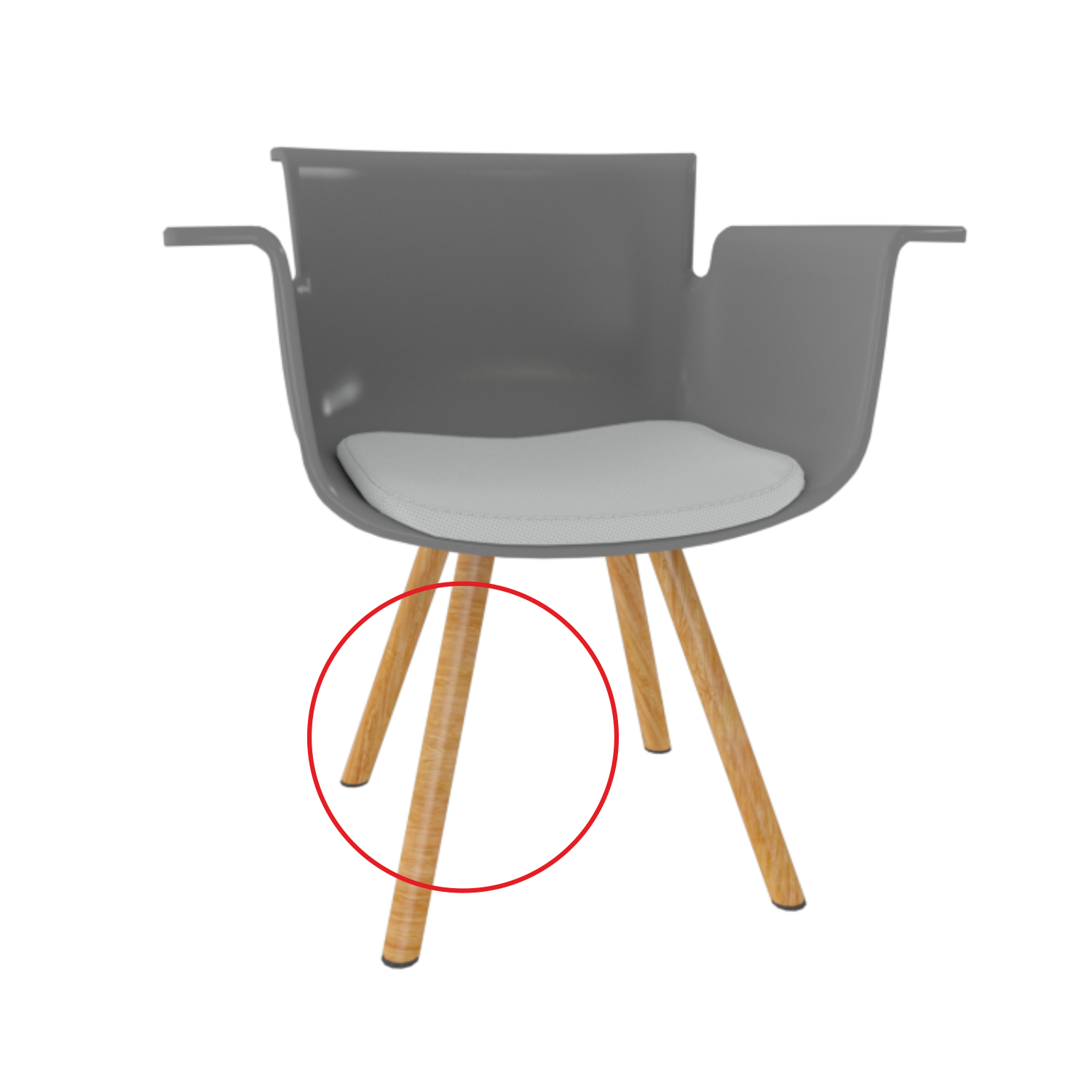
Size

Origin
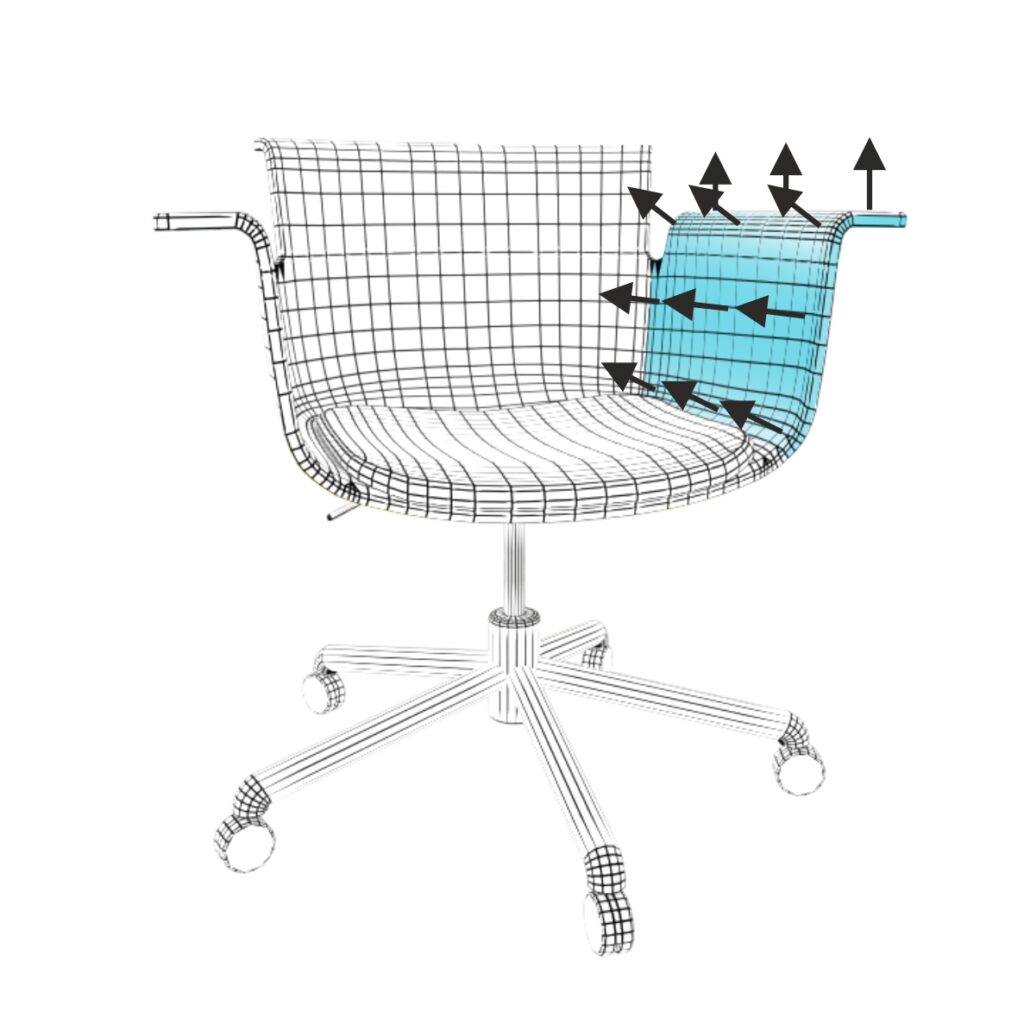
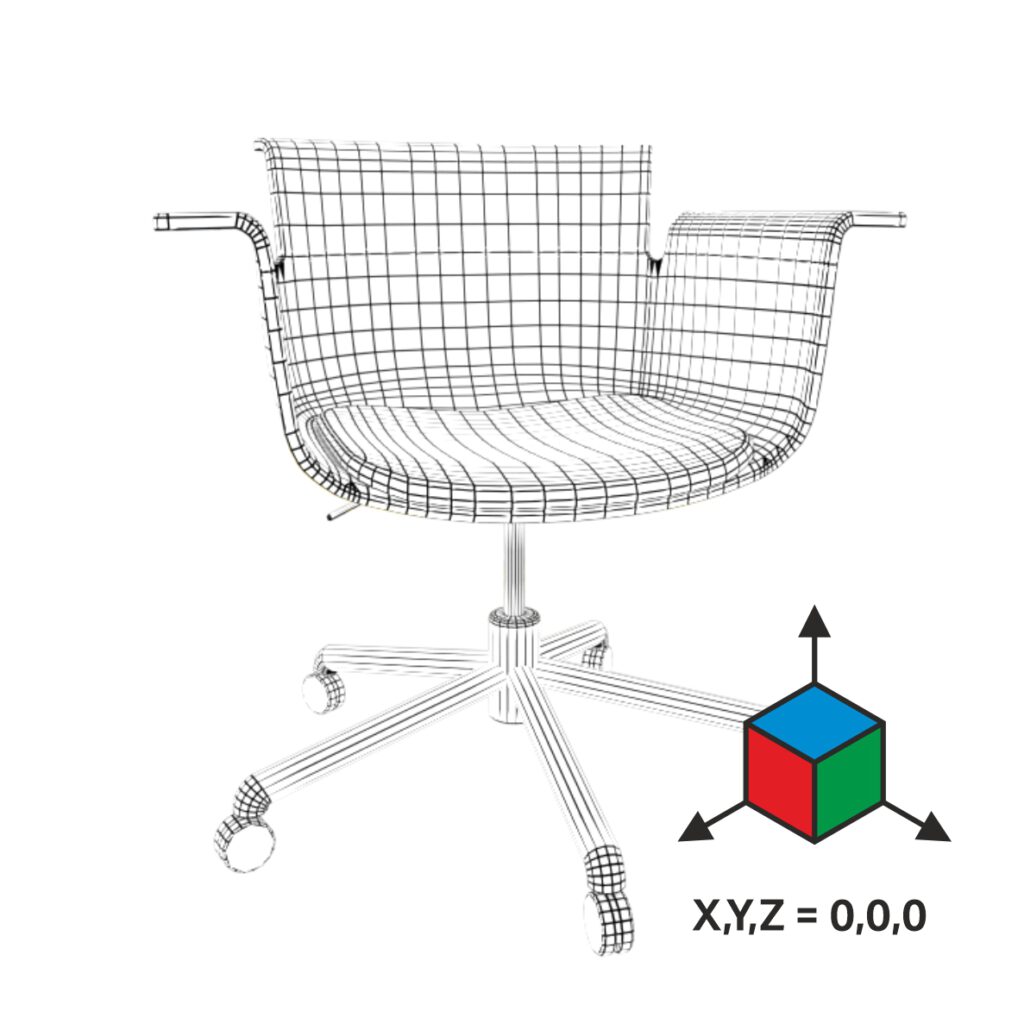
Object placement and orientation in a scene is based on its origin. Object parts position are relative to the internal origin position.
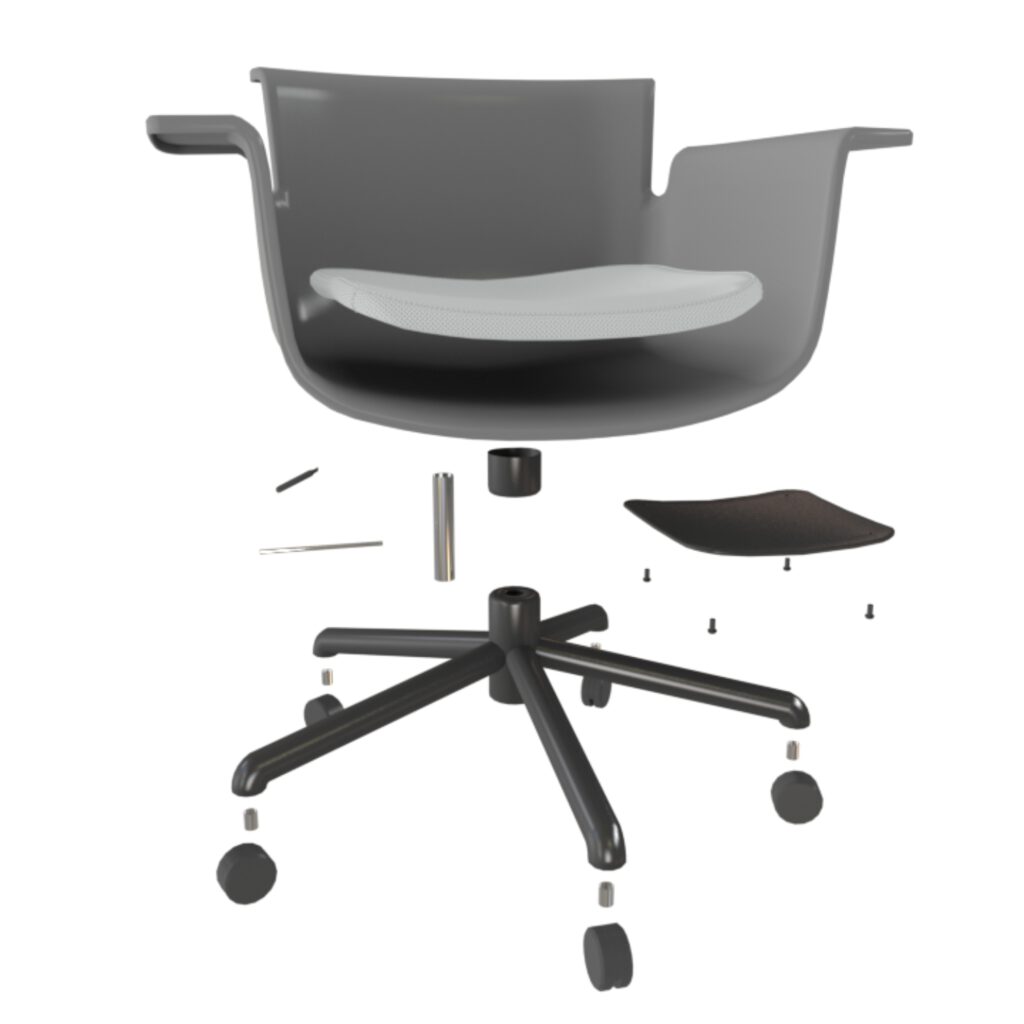

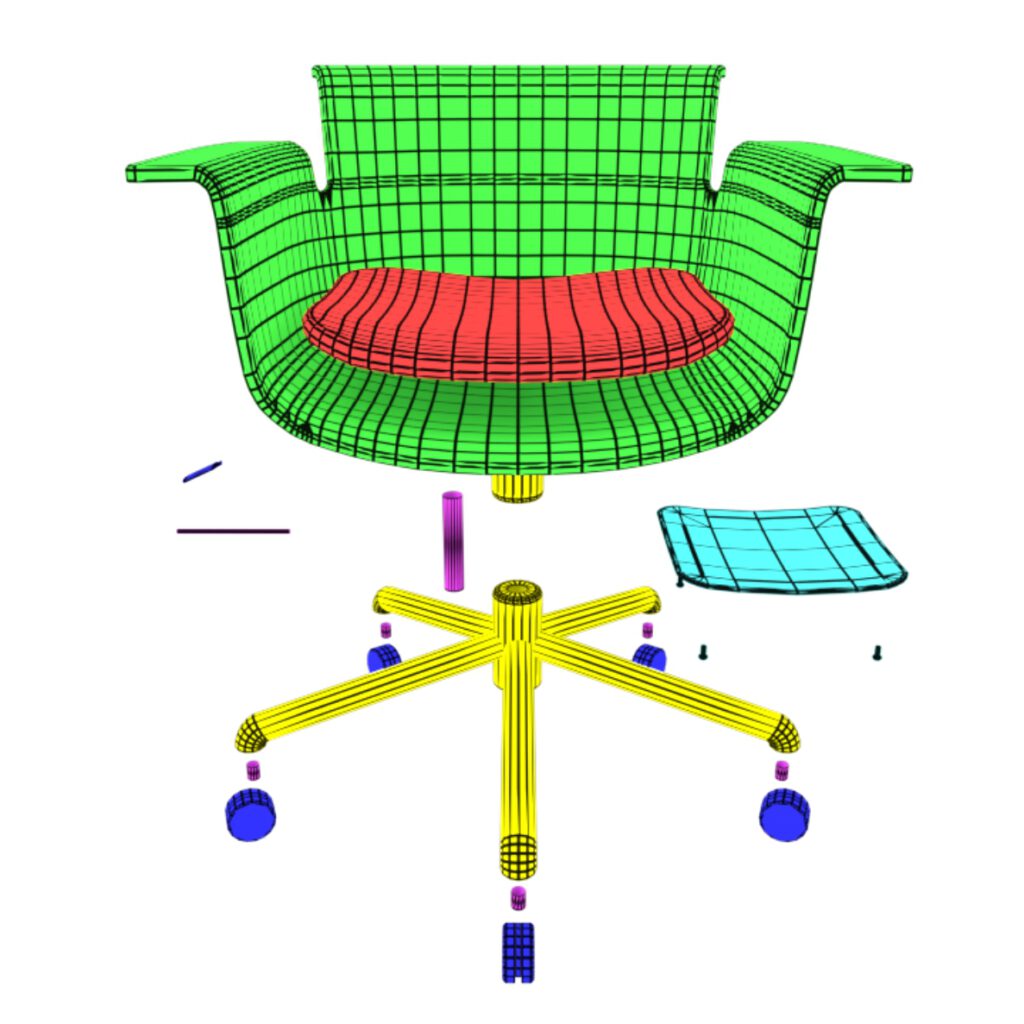
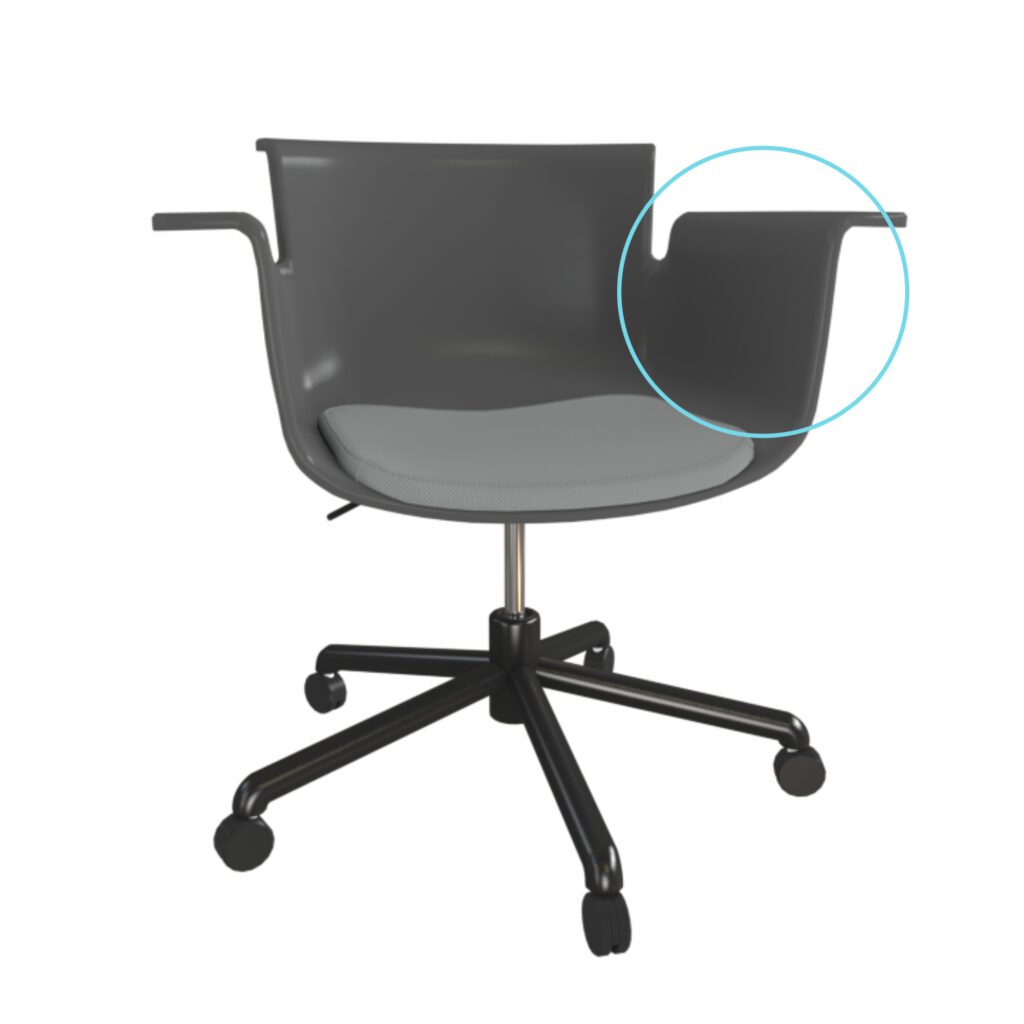
Structure
A model consists of multiple parts with seperate materials. To apply or change materials or parts, a proper object and naming structure is mandatory. Material channels need to be compatible with other softwares.
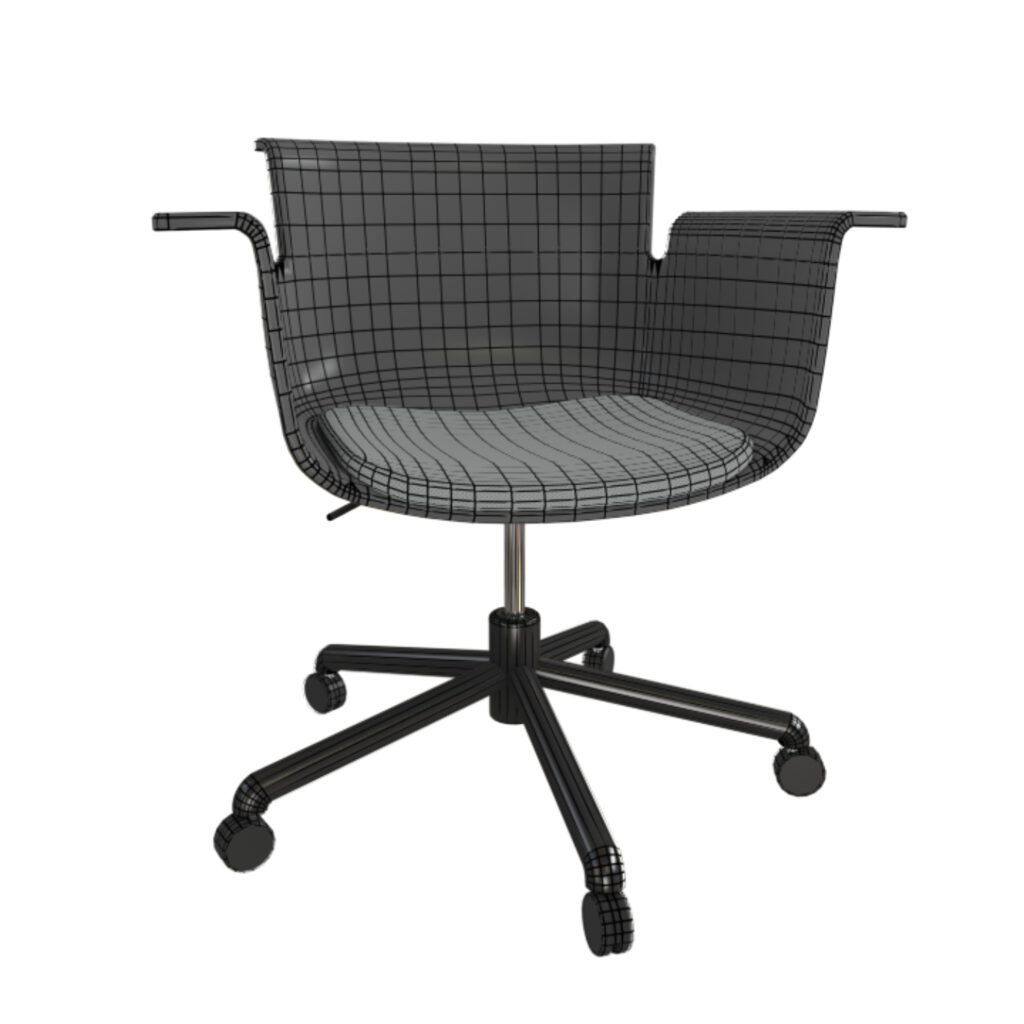
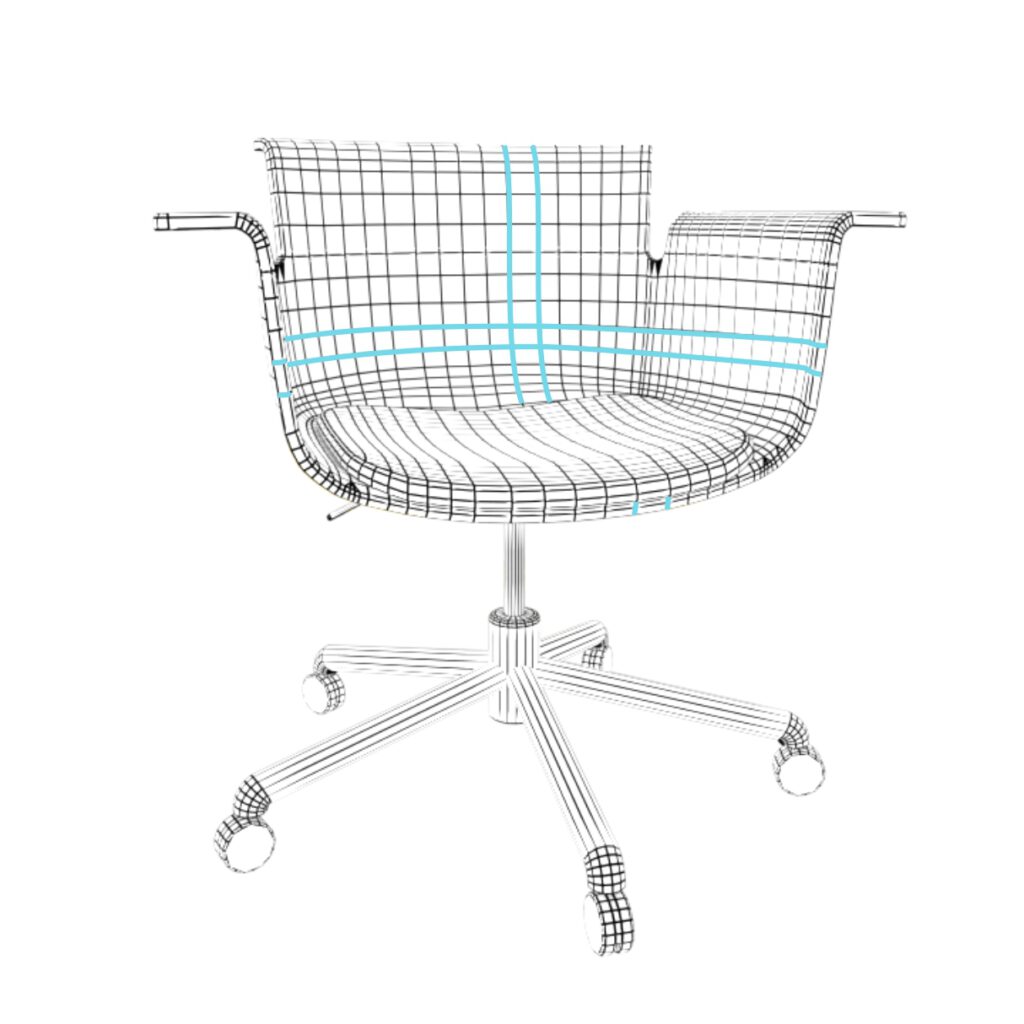


Geometry
Low polygonal geometry is resource friendly and essential for realtime presentation. Quad-based modeling is ideal for custom UV unwrapping and additional subdivision of surfaces.
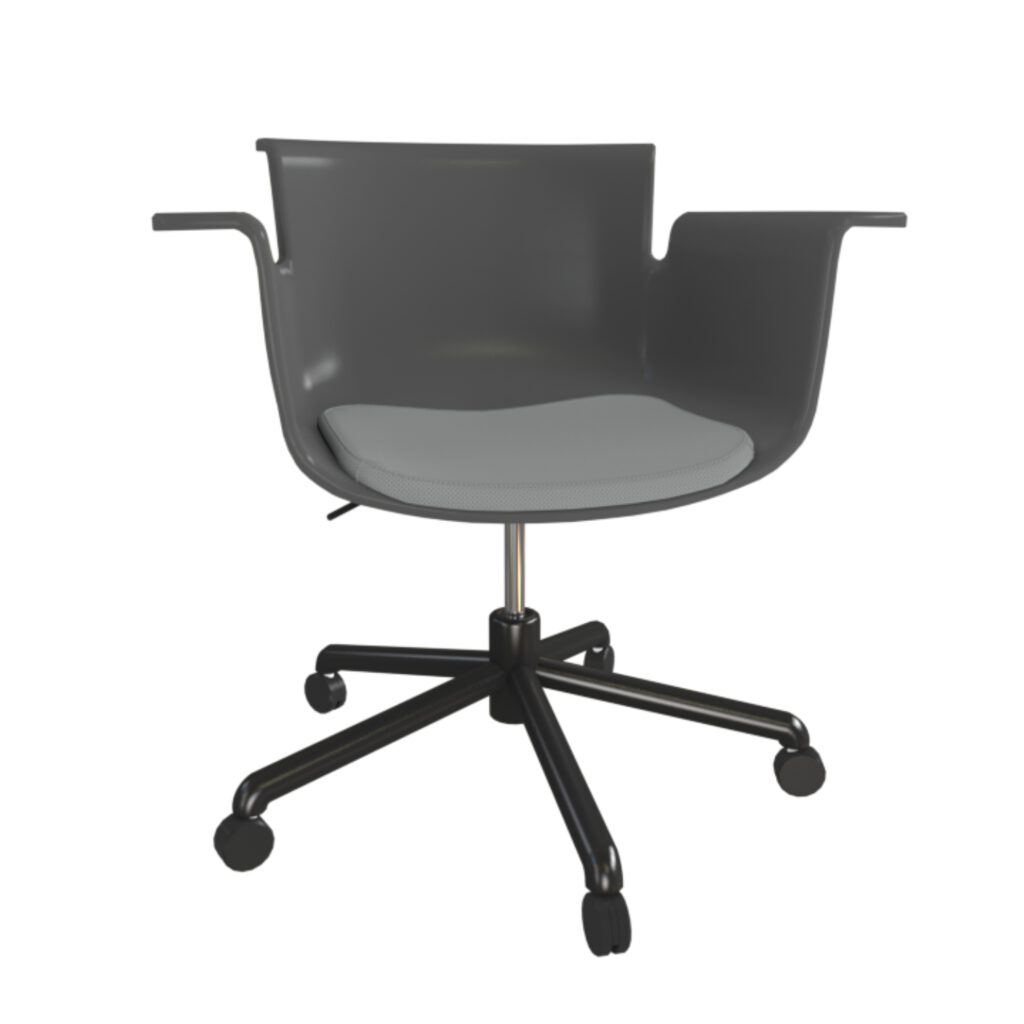

Textures
Textures represent material. Depending on use, images need to be tileable (without visual repetition) or high resolution. Surface appearance and detail (depth, structure) can be enhanced by additonal maps.
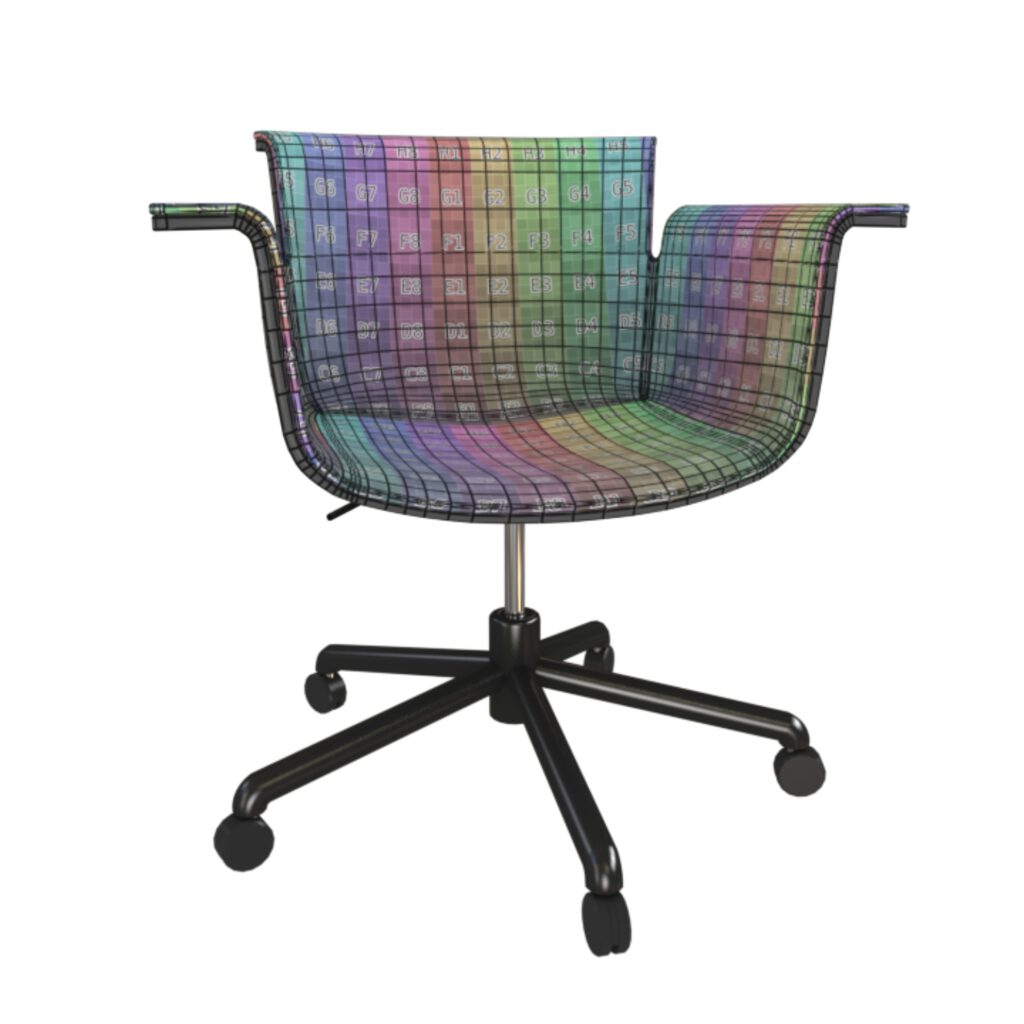

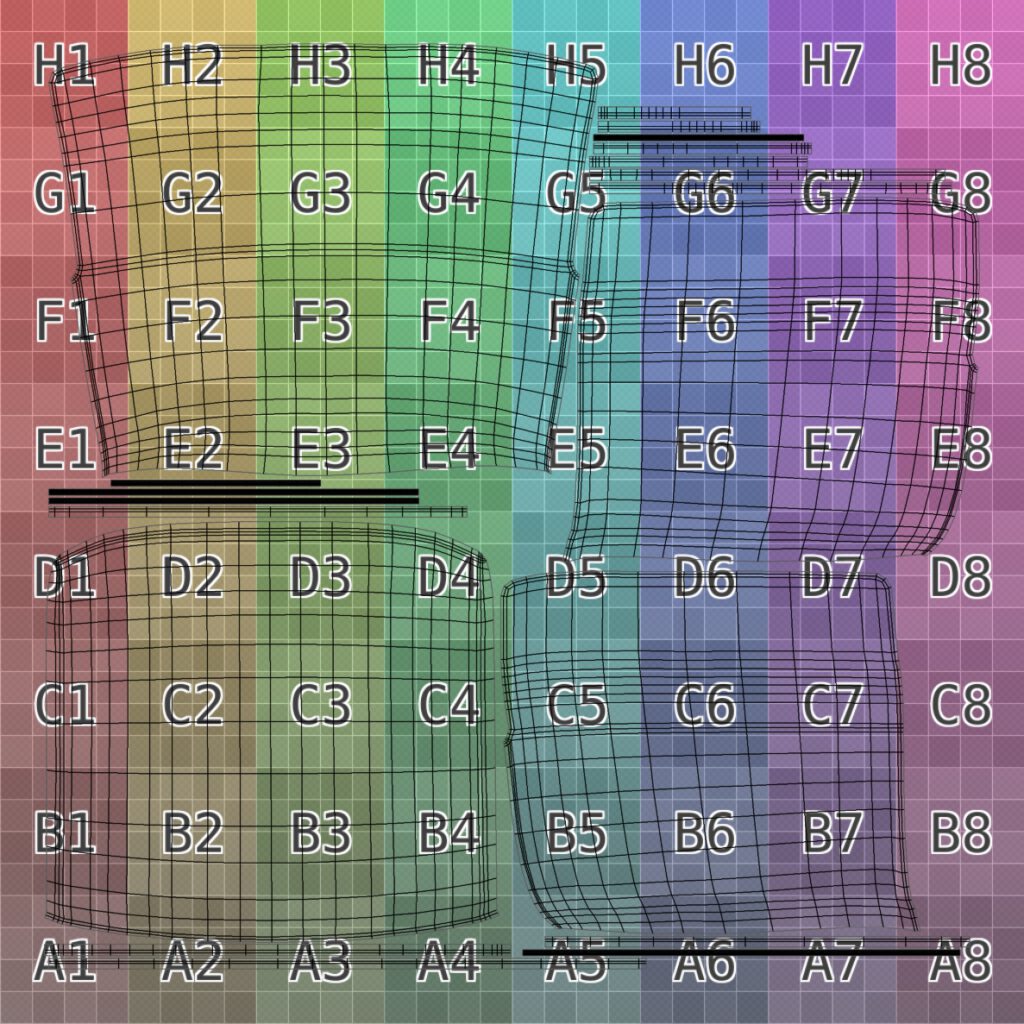
UV Unwrapping
UV surfaces are laid out flat and relaxed like sewing patterns to display unstreched textures on organic objects,
Kapitel / Stelle
Filetypes Pros and Cons
Many filetypes are commonly known and used for export. Kurze Erklärung, dann Empfehlung, welche genutzt werden sollten und warum.
| Filetype | Platform | Use | Compatibility | Embedded Materials | Normals Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWG | Multi | Import / Export | High | - | - |
| OBJ | Multi | Import / Export | High | - | |
| FBX | Multi | Import / Export | High | ||
| SKP | Sketchup | Planning / Visualization | Medium | ||
| IFC | BIM | Planning | Medium | - | - |
| GLB | webGL / VR / AR | Visualization | Low | ||
| MAX | 3D Studio Max | Visualization | Low | - |
Kapitel / Stelle
Platforms
3D models can be used in a wide variety of purposes. Visual communication, configurators, professional planning, quotation, customer experience and more.
Some platforms are free and accessible to millions of users, some are paid, some are limited to authorized personel only. Some are online, some are offline.
There is no one size fits all - it is important to identify effective platforms and have 3D content optimized for each platform.
3D Scanning
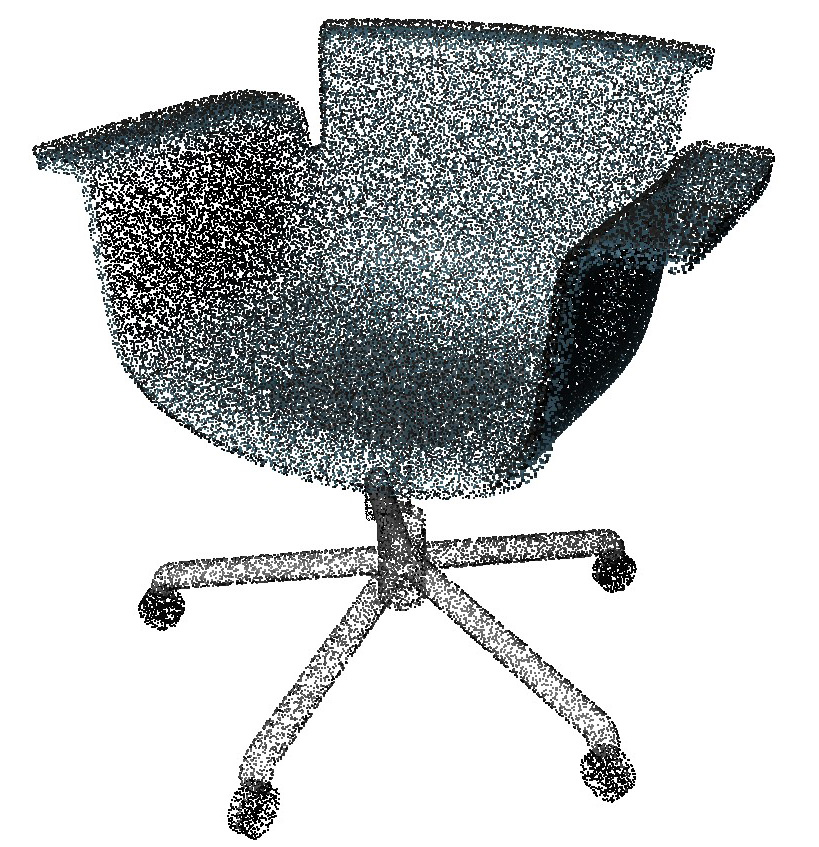

Is 3D scanning an option?
Short answer: No.
3D scanning has evolved a lot in the last time, from Apple's Iphone with lidar scanner to leading 3D scanners like Artec's Leo. They capture shape and material (as long as its not reflective or transparent) and give a good visual representation of the object. It can be processed and displayed digitally and it can be used to measure or create 3D models based on those scans.
But that's mainly it. The visual representation is not optimal, it is not resource friendly and it takes time to scan and clean up the scan. It will then not be useable in most cases. More important, it is only a simple representation. You wont be able to change parts or materials and materials cant be reflective or complex. And its almost impossible to create an "intelligent" model from it.
It is just one single 3D piece of data, no matter if its a piece of furniture, a person or an apple.
Truth about AR
Truth about AR
Augmented Reality (AR) is amazing! AR will be an essential part in our daily life, it will be everywhere and it will be as common as a smartphone is today.
But AR is not fully here - yet. There are applications that use AR, big players develop, implement and support AR (Apple, Google, Metaverse former Facebook, ..) and its available on many platforms. Many companies already tried and use it today (IKEA, Nike, Amazon, ..)
Still there are limitations that block the breaktrough of one of the main future medias: the biggest drawback is to look through a tiny smartphone screen to inspect 3D objects in AR.
Devices that naturally project digital content into the real world environment and allow interaction with this content are the future. Those devices already exist, but are not 100% there yet. They have limitations: field of view, visual quality, size, connectivity, price, content - all factors that limit the experience today. But companies invest massivly to change that, offer good devices for reasonable prices, which in turn will create a market for applications and reach a broad customer range. It will most likely be a cultural shift and a form of media that cannot be ignored.
What does that mean for 3D models in the furniture industry? CADform models are already prepared for what will come. Lightweight data with high visual quality. When the rocket takes off you will be all set and ready.
Or you are already planning to use AR or VR? Perfect. Lets get started.
